COLOR BANK SYSTEM
Color Bank
System
How to match colors
We strengthen the global competitiveness through an independent color mixing system and perfect color matching.
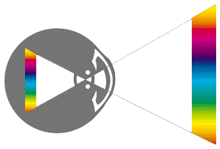
Light Theory
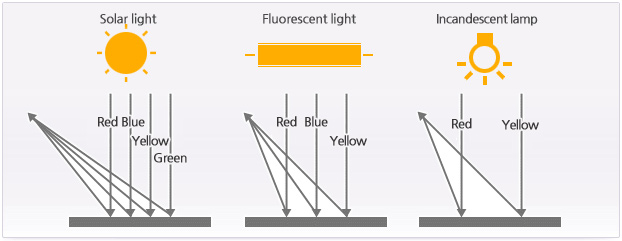
A color that we can see is decided according to the amount and kind of light wave returning from a surface. When the reflected light reaches the retina of eyes, it turns into an electronic shock and makes the brain distinguish colors. Also, the color can be recognized differently according to the light source because solar light has all lights (red, yellow, blue, green light) which can be seen in eyes but fluorescent light has only blue, yellow and red light, and incandescent lamp has only yellow and red light.
Hue circle theory
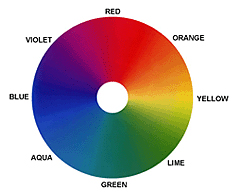
There are 8 different colors in the hue circle. In other words, color group 1 (basic color) has blue, red, yellow and green.
Color group 2 (mixed color) has purple, orange, yellowish green and bluish green.
Color group 2 is made by mixing two colors of color group 1. For example, purple is made with red and blue.
Orange is made with yellow and red. Yellowish green is made with yellow and green. Bluish green is the mixture of blue and green.
Adjacent colors : You get a vivider color when mixing neighbouring colors in the hue circle.
Complementary color, contrast color : A turbid color is created when mixing opposite colors in the hue circle. Also, color difference may occur depending on the light source.For example, using green to lessen red feeling, or using yellow to lessen blue feeling makes a turbid color.Thus try not to mix like this.
Terms
1) When comparing color difference, always distinguish it with 3 characteristics below.
- * Cast : Refers to red tone, yellow tone, blue tone, green tone, etc. A color has tones from 2 directions. Red can have blue or yellow tone and cannot have green tone. Orange can have red or yellow tone and cannot have blue or green tone.
- * Depth(Brightness) : For solid colors, depth stands for the degree of black and white. For metallic colors, it means brightness and darkness of the color.
- Chroma(Grayness) : Refers to vividness and turbidness of a color
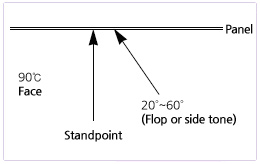
2) When comparing the difference of colors, the angle is classified by 2 angles as below.
- Front (Face) - See panel at an angle of 90˚.
- Side (Flop) - See panel at an angle of 20˚-60˚.
Consideration before color matching
1) There are several things to consider before color matching, especially for metallic colors.
| Thinning | Lack of thinner : vivid | Excessive thinner : turbid |
|---|---|---|
| Air | High : brighter | Low : dark |
| Room temperature | High : brighter | Low : dark |
| Spray gun | High air pressure : bright and soft | Low air pressure : dark and rough |
| Spraying method | Mist spray : bright | Wet-coat spray : dark |
| Thinner | Fast thinner : bright | Slow thinner : dark |
2) Three basic questions you need to answer before color matching
- How would you describe color difference? = What has been compared between car and paint?
- How much are you going to add? = It is better to add small amount than adding a lot.
Remember to match the color by adding small amount. - How will the color change when this toner is added?= A toner influences at least two characteristics of the color.
It affects color tone and depth, or color tone and chroma.
Rules for color matching
1) Follow 5 rules listed below.
- You can get a vivider color when mixing neighbouring colors in the hue circle.
- Avoid using a contrast color. It could be the reason of a muddy color and color difference.
- Avoid adding 2 colors at the same time. Set color tone first and then set brightness and chroma.
- Avoid using premixed colors. Only use original toners.
- If possible, use only half of mixed paint and store the remaining half to use it as a standard later.
2) Adjustment of color tone influences brightness and chroma.
- Color tone must be adjusted at the very beginning and get ready for the next step.
3) Color inspection
- Comparing area must be clean and glossy. Polish the comparing part.
- Check whether there is metallic or mica in the film. Is it on topcoat or basecoat? Is it uniform? Is it a stain?
- Check the paint inside the can. Apply it on a testing panel for accurate color matching.
Check the color after it is fully dried. - It is best to check the color under natural sunlight.
- Every color has to be compared at a same gloss level. Apply clearcoat on basecoat for a final check.
- Check the color from various angles(face and flop). A vehicle must be checked from an angle of 90°(face) and 20°-60°(flop).
- Check if color adjustment is possible.
- If it is not a broken panel, check if the color can be adjusted through blending process.
- Check if the color has been matched close enough.
※If you could answer 'Yes' to any of above questions, no further adjustment is needed.
Variables during color matching
| 1) How to make color bright | 2) How to make color dark |
|---|---|
| Use fast reducer. | Use slow reducer or add retarder thinner. |
| Use lots of reducer. | Use less reducer than normal. |
| Keep far distance between spary gun and panel. | Keep close distance between spray gun and panel. |
| Increase gun speed. | Decrease gun speed. |
| Increase flash time between applications. | Shorten flash time between applications. |
| Increase air pressure. | Decrease air pressure. |
| Increase fan width. | Decrease fan width. |
| Decrease discharge rate. | Increase discharge rate. |
| Use small fluid tip. | Use large fluid tip. |
| Increase the air flow or temperature. | Wet-on-wet application |
-
Product
-
COLOR-Q
-
Edu System
-
Customer support
NOROO Paint & Coatings Co., Ltd. (herein after referred to as “the Company”) regards the privacy of users as highly important and complies with all regulations concerning the “Act on Protection of Information and Promotion of Utilization of Information and Communications Network.”
By stating its privacy policy as shown below, the Company hereby informs users of the purpose and use of personal information provided by the user to the Company, and the measures taken for the protection of their personal information.
- 1. Personal information collected and the means of collection
- 2. Purpose of collection and use of personal information
- 3. Period of possession and utilization of personal information
- 4. Procedures and methods of discarding personal information
- 5. Disclosing personal information
- 6. Consignment of collected personal information
- 7. The rights of users and legal representatives and methods of exercising those rights
- 8. Install, manage and deny operation of device for automatic collection of personal information
- 9. Civil services with respect to personal information
- 10. Duty to notify
■ Personal information collected and the means of collection
A. Information we collect
• The Company collects the following data for the purpose of membership sign-ups, consultations, and service applications.
o When signing up for membership: Name, address, ID, password, phone number, e-mail, legal representative information for subscribers under the age of 14.
• Information collected through use of online services or the processing process: use record, access log, cookies, connecting IP information, unruly use, and others.
B. Means of collecting personal information
• Personal information is collected through the website, letter, message boards, e-mail, event entries, delivery request forms, phone, fax, and generated data collection tool.
■ Purpose of collection and use of personal information
The Company collects personal information for the following purposes and use.
• Member management
Identify user to access members-only services, verify user, prevent unauthorized use, check membership subscription, validate age, confirm consent/agreement from legal representative for users under the age of 14, handle complaints and civil affairs, and deliver notices.
• Marketing and promotional use
Delivery of events and unsolicited advertisements; gain a statistical understanding of the members’ frequency of access to and use of site.
■ Period of possession and utilization of personal information
As a general rule, once the personal data has fulfilled the purposes for which they were collected, they are to be immediately discarded. Except for the following that will be retained for certain periods for reasons noted below.
A. Information held according to the Company’s internal policies
Even when a member has canceled his/her membership, the member’s personal information may be retained for 6 months from the date of cancelation in order to resolve future disputes, to cooperate with the requests of law enforcement agencies, and to prevent the recurrence of fraudulent uses by unruly members.
B. Grounds for holding personal information according to applicable statutes
If retention of personal information is deemed necessary to operate in accordance to the provisions of relevant laws and regulations, including the Act on Consumer Protection in Electronic Commerce, then they will be held in possession by the Company for a certain period of time set by the relevant laws as noted below.
• Records related to contracts or withdrawal of subscription:
o Purpose of possession: Act on Consumer Protection in Electronic Commerce
o Possession period: 6 months
• Records related to consumer complaints or dispute settlement
o Purpose of possession: Act on Consumer Protection in Electronic Commerce
o Possession period: 3 years
• Records of log
o Purpose of possession: Protection of Communications Secrets Act
o Possession period: 6 months
■ Procedures and methods of discarding personal information
As a general rule, once the personal data has fulfilled the purposes for which they were collected, they are immediately discarded. The procedure and method to discard is detailed below.
• Discarding procedure
Following the cause for information protection according to the internal policies or related statutes, once the personal data has fulfilled the purposes they will be transferred to a separate database(DB) (or filed separately in a folder if in paper form), then it will be discarded after a certain period of time. Personal information that is transferred to a separate DB will not be used for any other purposes except in the case of the law.
• Discarding method
Use technical method to stop reproduction of personal information saved in electronic form.
■ Disclosing personal information
As a general rule, the Company shall not disclose user’s personal information to any external party except for the cases below.
• Prior consent from user
• Following the legislation rule or when law enforcement agencies require such information for investigative purposes during the process as prescribed by the law.
■ Consignment of collected personal information
For the provision of services, the Company consigns collected personal information to specialized companies detailed below.
• Consignee: [Name of delivery company]
• Details of consignment: [Delivery company’s consignment details]
• Consignee: [Name of payment gateway provider]
• Details of consignment: [Payment gateway provider’s consignment details]
■ The rights of users and legal representatives and methods of exercising those rights
• The user may view or edit his/her personal information and request to terminate membership at any time.
• To view or edit a user’s personal information, click on ‘Edit Personal Information’ (or ‘Edit Member Information’) and to cancel subscription (terminate membership) click on ‘Terminate Membership.’ Upon clicking, you’ll be directed to an identification process before you can directly access, correct, or cancel membership.
• User may contact the chief privacy officer by letter, telephone or email, and necessary actions will be taken.
• Should a user request corrections on errors of personal information, the Company shall not use or provide any personal information until a correction is made. In addition, if the wrong personal information has already been provided to a third party, the Company shall immediately notify them so that a proper correction can be made.
• If personal information is canceled or deleted upon request of user, the Company will comply with the terms specified under “Period of possession and utilization of personal information,” and prohibit disclosure or use for any other purposes.
■ Install, manage and deny operation of device for automatic collection of personal information
The Company uses ‘cookies’ that frequently save and retrieve your information. A cookie is a very small text file that the server, used to operate the Company’s website, sends to your browser. The file is saved in the hard disk of your computer.
The Company uses cookies for the following purposes:
• Use and purpose of cookies
o To analyze the frequencies of a member and non-member’s visit, understand user’s preferences and interests and track user’s footprints, and carry out target marketing and provide customized service by checking level of participation in various events and number of visits.
o You have the right of choice in regards to the installation of cookies. Accordingly, you may allow all cookies by modifying your cookie settings, go through a confirmation process whenever a cookie is saved, or refuse to have all cookies saved.
• Settings to reject establishment of cookies
o To reject establishment of cookies, select options on your web browser and change your settings to allow all cookies, go through a verification process before saving cookies, or reject to save all cookies.
o Example (For Internet Explorer)
- Go to ‘Tools’ located on the top of Web Browser > Internet Options > Privacy
o However, there may be certain difficulties in using the services if you reject the installment of cookies.
■ Civil services with respect to personal information
To protect your personal information and deal with complaints related to personal information, the Company has appointed the following department and chief privacy officer.
• Principal Privacy Officer
Name: Rando Kim
Department: Overseas Business Department
Phone Number: +82-31-467-6286
E-mail: kimrd@noroo.com
• Chief Privacy Officer
Name: Chul Jin Park
Department: Overseas Business Department
Phone Number: +82-31-467-6283
E-mail: cjpark@noroo.com
• You may report all complaints related to privacy protection, in using the Company’s service, to the chief privacy officer or the department in charge.
• The Company shall provide prompt and sufficient answers to your report.
• For further consultation or report on other privacy infringements, contact the following the following agencies.
o Privacy Rights Violation Complaint Center (privacy.kisa.or.kr / +82-118)
o Cybercrime Investigation Department, Supreme Prosecutor’s Office (www.spo.go.kr / +82-2-3480-2000)
o Cyber Bureau, National Police Agency (www.ctrc.go.kr/ +82-182)
■ Duty to notify
The Company shall notify users of any changes to this privacy policy through the website (or through individual notifications).
• This privacy policy will be enforced starting October 1, 2016.
Article 1 (Purpose)
The purpose of the following Terms and Conditions of Use(‘T&C’) is to establish guidelines on rights, duties and responsibilities of website Users utilizing the internet-related services (hereinafter referred to as the ‘Services’) provided by the website (hereinafter referred to as the ‘Site’) operated by company (NOROO Paint & Coatings).
※ 『Unless transactions contradict its properties, the following terms apply to e-commerce transactions utilizing methods of PC communication, wireless and others』
Article 2 (Definition)
①‘Site’ refers to a virtual business site established by company to trade goods or services (hereinafter referred to as ‘Goods and Services’) using computers and information communication facilities to provide Goods and Services to Users. The term can also be defined as a company operating a website.
②‘User’ refers to a Member and Non-Member who has accessed the ‘Site’ to use the services provided by the ‘Site’ in accordance with this T&C.
③‘Member’ refers to a User who uses the services provided by the ‘Site’ by subscribing for Membership.
④‘Non-Member’ refers to a User who uses the services provided by the ‘Site’ without subscription.
Article 3 (Display, Explanation and Amendment of Terms and Conditions of Use)
① The ‘Site’ shall, for easy recognition by Users, display the contents of this T&C, name of company, business address(including an address handling customer complaints), phone number, fax number, email address, and the name of personal information manager on the main page of the ‘Site’. Only the content of this T&C can be displayed though a link page.
② Prior to User’s final agreement to this T&C, the ‘Site’ shall provide a separate link or pop-up screen to obtain User’s verification on the terms of important details.
③ The ‘Site’ may make amendments within the permissible range without violating applicable laws such as the 「Act on Consumer Protection in Electronic Commerce」, 「Regulation of T&C」, 「Framework Act on Electronic Commerce and Electronic Document」, 「Electronic Financial Transaction Act」, 「Electronic Signature Act」, 「Act on Protection of Information and Promotion of Utilization of Information and Communications Network」, 「Door-To-Door Sales Act」, 「Framework Act on Consumers」 and other related Consumer Protection Laws.
④ The ‘Site’ shall specify the effective date and the reasons for amendment of the terms and have post on the initial screen for 7 days prior to effective date until the day before the effective date.
If the amendment is modified to the User’s disadvantage, then the ‘Site’ shall grant at least 30 days of grace period for notice. In this case, the ‘Site’ shall clarify the ‘before and after’ changes in an ‘easy-to-understand’ manner.
⑤ When the ‘Site’ makes an amendment to the T&C, the modified T&C shall be applied only to contracts concluded after the effective date, whereas all contracts concluded before the effective date will remain under the provisions of the old T&C. However, if the User who has already signed the contract wishes to have the amendments administered, then the User may send his/her intent to the ‘Site’ and acquire consent from the ‘Site’ within the notice period stated in Clause ③ and it shall be applied accordingly.
⑥ Any information not specified and interpreted in this T&C shall be in accordance with the e-commerce Transaction Guidelines and Related Consumer Protection Acts provided by the Fair Trade Commission and other applicable Consumer Protection Laws and Regulation of T&C Act.
Article 4 (Provision & Replacement of Service)
① The ‘Site’ shall perform the following duties:
1. Provide information regarding Goods and Services.
2. Other duties designated by the ‘Site.’
② The ‘Site’ may replace Goods and Services provided in future T&C in the event that Goods and Services are sold out or technical specifications are revised. In this case, the ‘Site’ shall immediately announce the replacement of Goods and Services and the date of application on the page where present Goods and Services are displayed.
③ In the event that Goods and Services are replaced because of a change in technical specifications or when Goods and Services are sold out, the ‘Site’ shall immediately notify the cause of replacement to the Users.
Article 5 (Suspension of Service)
① The ‘Site’ may temporarily suspend its services as a result of the following reasons: maintenance of computers and telecommunications equipment, replacement or damage repairs, and interruption of communication.
② The ‘Site’ shall compensate User or any Third Party Member of damages caused by the temporary suspension of services due to reason(s) detailed in Clause ①. However, this shall not apply if the ‘Site’ proves that such event is not caused by its intention or negligence.
③ In the case of a conversion of business item, abandonment of business, merging between businesses and for other various reasons, the ‘Site’ shall notify the consumer as specified in Article 8 and reward consumer in accordance with the conditions suggested by the original ‘Site.’ However, if the ‘Site’ does not advise such standard of compensation, the ‘Site’ shall pay Users for their mileage or reserve in kind.
Article 6 (Membership)
① The User shall apply for Membership by expressing his/her intent to agree to this T&C after filling out the form designated by the ‘Site’ with Member’s personal information.
② The ‘Site’ shall register all Users who apply for Membership in the manner stipulated in Clause ① unless the User is not engaged in one of the following issues:
1. After the applicant has lost Membership for reasons indicated in Article 7 Clause ③, the applicant may acquire approval to re-subscribe for Membership three years after the loss of Membership.
2. Entry of false information or omission in the registration form.
3. If deemed that registering the User would present technical difficulties to the ‘Site.’
③ Establishment of Membership becomes effective at the time that the Member receives the ‘Site’s approval of Membership.
④ In due course of time, the Member shall update the ‘Site’ with any changes to his/her account information through the methods of editing personal information.
Article 7 (Withdrawal from Membership & Loss of Eligibility)
① Members of the ‘Site’ may request, at any time, to withdraw from Membership and the ‘Site’ shall immediately process the request.
② The ‘Site’ may limit or suspend Membership for the following reasons:
1. Entry of false information or omission in the registration form.
2. If Member interferes with others to use the ‘Site’ or threatens the order of e-commerce (such as the illegal use of personal information).
3. If Member uses the ‘Site’ to act against public order and morals prohibited by the law and this ‘T&C.’
③ The ‘Site’ may forfeit Membership of the Member whose Membership was suspended or limited, if the same actions are repeated twice or more, or if the cause is not corrected within 30 days.
④ When the ‘Site’ forfeits Membership, all information will be cancelled. Prior to cancellation, the ‘Site’ shall notify the Member and give at least 30 days or more to grant an opportunity to explain the cause.
Article 8 (Notification to Members)
① Any notifications from the ‘Site’ will be sent to the email address designated in advance by the Member during registration.
② In the event of sending notifications to unspecified Members, a display of notifications on the notice board on the website for 1 week or more may replace sending emails. However, the ‘Site’ shall send individual notice to a Member in regards to matters which may have a significant influence in his/her transaction.
Article 9 (Protection of Personal Information)
① The ‘Site’ collects a minimum amount of information necessary to provide the services.
② At the time of applying for Membership, a minimum amount of specified personal information is collected for the fulfillment of obligation in regards to relevant laws and legislation.
③ The ‘Site’ shall obtain consent from User to collect and use personal information by notifying User with the aim/purpose of collection and use.
④ The ‘Site’ shall not use the personal information outside their intended purpose. In the event of an uprising of a new use or when disclosing to third parties, the ‘Site’ shall notify the purpose of use and obtain consent from User during the stage of use or disclosure. But, there are exceptions for cases regulated in the relevant laws and legislations.
⑤ In the event that the ‘Site’ is required to acquire the approval of User by Clause ② and ③, the ‘Site’ shall specify its personal information manager (affiliation, name, phone number, other contact information), purpose of collection and use of information, information about Third Party (recipient, purpose of provision and the information to be provided), and the provisions stipulated in Clause ② of Article 14 of the 「Act on Protection of Information and Promotion of Utilization of Information and Communications Network」. The User may at any time cancel his/her approval.
⑥ User may, at any time, request for confirmation and correction of error in their personal information possessed by the ‘Site,’ and the ‘Site’ shall be responsible for taking any necessary measures without any delay. In the event that a User requests for the correction of an error, the ‘Site’ shall not use the applicable personal information until error is corrected.
⑦ For protection of personal information, the ‘Site’ shall limit the number of persons handling personal information to a minimum, and shall be responsible for disclosure of personal information to third parties without consent of the User.
⑧ The ‘Site’ or any Third Parties who received personal information from the ‘Site,’ shall without any delay destroy all personal information once the purpose of collection has been achieved.
⑨ The ‘Site’ shall not have the agreement form regarding the collection∙use∙disclosure of personal information set to be filled out in advance. The ‘Site’ must specify services that will be restricted if User does not agree to the collection∙use∙disclosure of personal information, and the ‘Site’ shall not limit services or refuse to accept Membership applications on the basis of User’s refusal to agree to collecting∙using∙disclosing of personal information that do not include the collection of compulsory information.
Article 10 (Obligations of the ‘Site’)
① The ‘Site’ shall not take any actions against public policy or actions restricted by the law and this T&C. The ‘Site’ shall put its best efforts in providing Goods and Services on a stable basis in accordance with the provisions in this T&C.
② The ‘Site’ shall be equipped with a security system to protect personal information of Users (including credit information) and provide a safe environment for Users to use the online services.
③ In accordance with Article 3 of the Law related to 『Fairness of Display and Advertisement』, the ‘Site’ shall be responsible to compensate User(s) if damages were caused by displaying or adding unjust or unreasonable advertisement for certain Goods and Services.
④ The ‘Site’ shall not send any profit-making emails which are not wanted by Users.
Article 11 (Obligations for ID & Password of Member)
① Member shall be responsible for the management of his/her ID and password, except for the case in Article 9.
② Member shall not allow any Third Party to use his/her ID and password.
③ When a Member recognizes that his/her ID and/or password is stolen or is being used by a Third Party, the Member shall immediately notify the ‘Site’, and follow the instructions of the ‘Site.’
Article 12 (Obligations of User)
Users shall avoid the following actions:
1. Register false information at the time application or revision of information
2. Use others’ personal information
3. Change information displayed on the ‘Site’
4. Remit or display information (computer program and others) other than the information put on by the ‘Site’
5. Infringe copyright or intellectual property rights of the ‘Site’ or the Third Party
6. Take any action that harms the reputation and interrupts the operation of the ‘Site’ or a Third Party
7. Disclose or display any information containing indecent or violent message, video, voice, and other information going against good public order and morals.
Article 13 (Relationship between Linking Site & Linked Site)
① In the event that the main Site and the sub-Site are linked with a hyperlink (ex. the subject of hyperlink includes text, image and video), the former is called as the Linking Site (Website) and the latter is called as the Linked Site (Website).
② If the Linking Site specifies and notifies the fact that it is not responsible for any transaction with the User for any Goods and Services independently provided by the Linked Site on the initial page of the website of the Linking Site or a pop-up window, then the Linking Site is not responsible for such transaction.
Article 14 (Copyright & Limitation of Use)
① The copyright and other intellectual property rights for the works produced by the ‘Site’ shall belong to the ‘Site.’
② The User may not use or cause any Third Party to use information with intellectual property rights belonging to the ‘Site’ for reproduction, transmission, publishing, distribution, broadcasting or other profit-making use without prior consent of the ‘Site.’
③ The ‘Site’ shall notify the User when using the copyright belonging to the applicable User in accordance with mutual T&C.
Article 15 (Resolution of Dispute)
① The ‘Site’ shall apply and reflect the opinion or complaint made by User(s), and install and operate a process for compensation of consumers’ damages.
② The ‘Site’ shall give priority to any opinion or complaint made by User(s). However, in the event that it may not be able to promptly deal with the matter, the ‘Site’ shall notify the User with the cause and the final settlement schedule.
③ When a User files for Remedy of Damage regarding a dispute between the ‘Site’ and the User, the matter may be commissioned for arbitration by the Fair Trade Commission or a Dispute Conciliation Services Organization selected by the City Mayor.
Article 16 (Jurisdiction & Governing Law)
① All e-commerce related lawsuits between the ‘Site’ and a User shall be in accordance with the address of the User at the time of indictment. If an address is nonexistent, then the lawsuit shall fall under exclusive jurisdiction of the district court in the vicinity of User’s place of residence. In the event that the address or residence of the User is not clear at the time of indictment or if User is a foreign resident, the lawsuit shall be filed to the competent court on the Civil Procedures Code.
② Any and all e-commerce-related lawsuits between the ‘Site’ and a User shall be governed by the law of the Republic of Korea.

